Austausch im Alpenraum
Montag, 02.07.2025, geschrieben von Gudrun Bruckner

Austausch mit anderen Schutzgebieten im Alpenraum
Der direkte Austausch mit Kolleg:innen aus anderen Schutzgebieten im Alpenraum ist enorm wertvoll – besonders wenn genug Zeit für persönliche Gespräche bleibt. Fragen wie „Wie macht ihr das eigentlich?“, „Wie läuft das bei euch?“ oder „Habt ihr dazu ein Monitoring?“ eröffnen den Raum für praxisnahe Einblicke. Die Themen reichen von Neophyten-Management über den Schutz von Raufußhühnern bis hin zu hochtechnologisierten Biodiversitätsmonitorings.
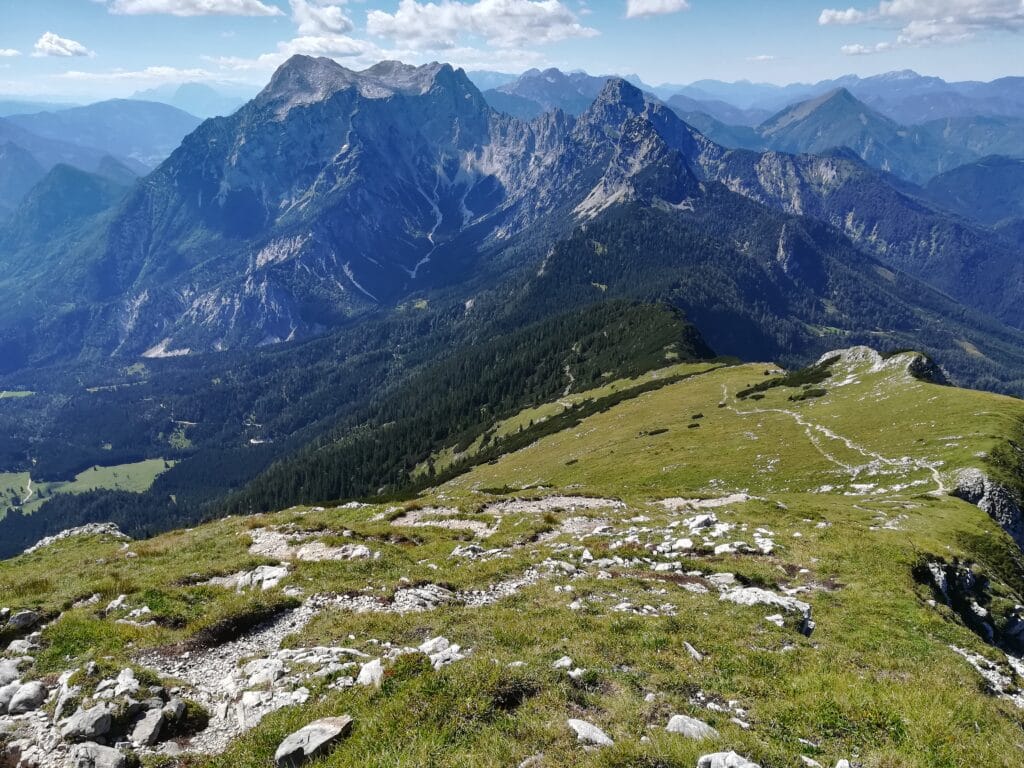
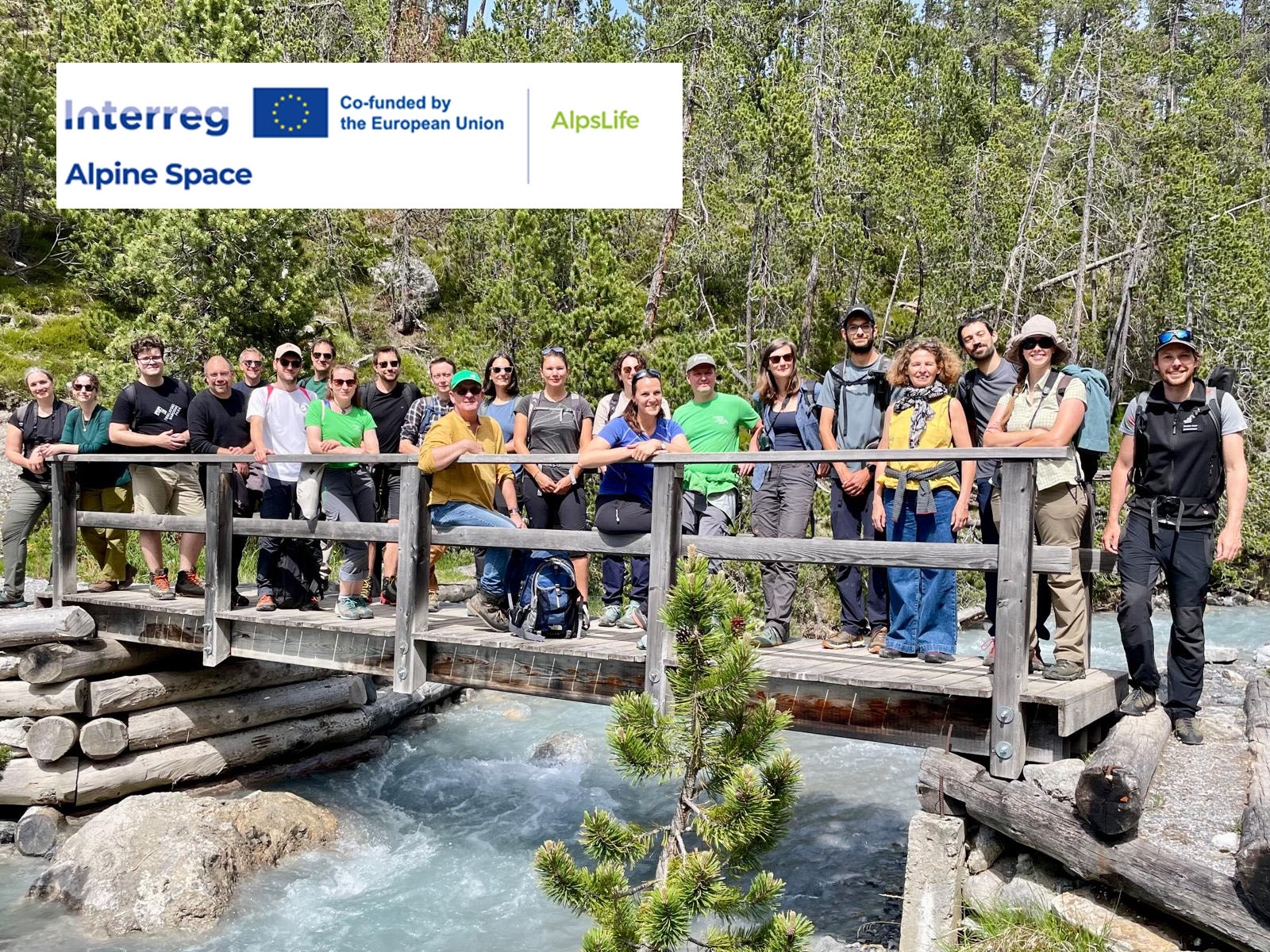
Mitte Juni traf sich das AlpsLife-Konsortium in Zernez im Schweizerischen Nationalpark. Eine Exkursion bot spannende Einblicke in die Arbeit der Schweizer Kolleg:innen vor Ort. Zudem informierten die Arbeitspaket-Leitenden über den aktuellen Stand des Projekts, und erste Ergebnisse wurden vorgestellt. In einer intensiven Workshop-Session wurden schließlich wichtige Weichen für die zukünftige Entwicklung von AlpsLife gestellt.
Das Potenzial dieses Austauschs ist groß: Wir müssen nicht dieselben Fehler wiederholen, können voneinander lernen und Methoden sowie Daten abgleichen. So entsteht langfristig eine bessere Vergleichbarkeit der Biodiversitätsdaten im gesamten Alpenraum – ein entscheidender Schritt für großflächig wirksamen Naturschutz.
MASTERARBEIT: Naturnacht
Montag, 02.07.2025, geschrieben von Gudrun Bruckner
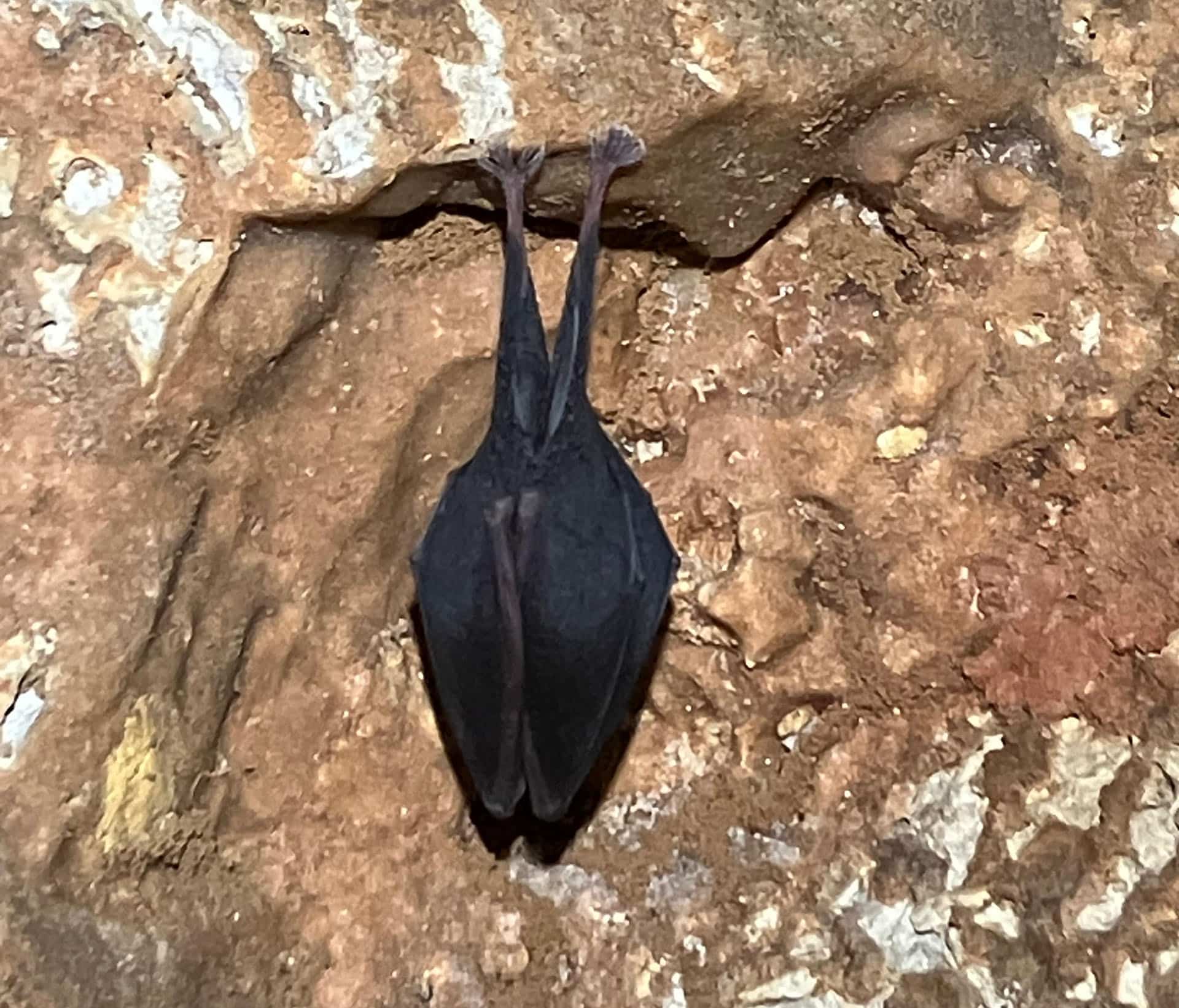

Gudrun Bruckner untersuchte im Rahmen ihrer Masterarbeit die naturschutzfachliche Relevanz von natürlicher Dunkelheit unter Verwendung lichtempfindlicher Fledermausarten (Myotis and Rhinolophus Arten) als Indikatoren. Als Untersuchungsgebiet diente das in Zentralösterreich liegende Planungsgebiet des ersten International Dark Sky Reserves Österreichs (Naturnachtgebiet Eisenwurzen). Es wurden GIS-Analysen von Fledermaus- und Lichtverschmutzungsdaten durchgeführt, um festzustellen, wie stark Population oder Habitate betroffen sind. Außerdem wurden Strategien zur Kunstlichtminderung erarbeitet. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass sich derzeit nur etwa 10 % der Fledermaus-Wochenstuben innerhalb der vorgeschlagenen Kernzone des Dark Sky Reserves befinden. Darüber hinaus sind fast 47 % aller Wochenstuben der untersuchten Arten direkt von Lichtverschmutzung betroffen, bei einem Radius von 2,5 km sind es sogar 68 %. Praktische Herausforderungen bestehen bei der Erweiterung der Kernzone, so dass umfassendere Lichtmanagementstrategien unerlässlich sind. Methoden wie die Einführung von Beleuchtungsplänen, die Anpassung von Lichtfarbe und Intensität sowie die Priorisierung von fledermausempfindlichen Bereichen sind entscheidend für die Minimierung ökologischer Auswirkungen. Zusammenfassend zeigt diese Arbeit, dass auch bei begrenzter Datenverfügbarkeit strategische Schutzmaßnahmen gegen Lichtverschmutzung möglich sind. Die wachsende internationale Aufmerksamkeit und die Entwicklung von Rahmenbedingungen zur Eindämmung von Lichtverschmutzung geben Hoffnung auf großflächig wirksame Maßnahmen. Letztlich wird die strategische Bekämpfung der Lichtverschmutzung erhebliche ökologische und gesellschaftliche Vorteile bringen.
Die Arbeit ist hier nachzulesen:
https://www.parcs.at/npg/mmd_fullentry.php?docu_id=55466
Ausschreibung Doktorat
Montag, 31.03.2025, geschrieben von Alexander Maringer

Stellenausschreibung Doktoratsprogramm für alpine Quell-Forschung
Die Alpen beherbergen eine hohe Geo- und Biodiversität und sind stark von vergangenen, gegenwärtigen und zukünftigen Umweltveränderungen betroffen. In dem neuen Doktoratsprogramm der Universität Salzburg wird eine hochmoderne, interdisziplinäre Forschungs- und Ausbildungsagenda verfolgt. Mit einem Konsortium, das Wissenschaftler:innen aus verschiedenen Disziplinen wie Geologie, Geomorphologie, ökologischer und evolutionärer Botanik und Zoologie sowie Geschichte umfasst, stellen wir die Fragen: (1) Welche Auswirkungen haben Umweltstörungen auf Geo- und Biosysteme und wie übersetzen sich Veränderungen in einem System auf das andere System? (2) Welche Rückkopplungsschleifen bestehen zwischen Geo- und Biosystemen? (3) Welche vergangenen und zukünftigen Dynamiken können abgeleitet werden, wenn Daten aus Geowissenschaften, Biowissenschaften und Geschichte integriert werden?
Projekt 3 „Hydrogeological patterns and alpine spring metacommunities“ wird auch zum Teil seinen Schwerpunkt im Nationalpark Gesäuse haben. Der Starttermin ist flexibel zwischen Oktober 2025 und Januar 2026. Die Dissertationsstelle wird für 3,5 Jahre voll finanziert.
Ein Adler macht noch keinen Sommer
Dienstag, 18.03.2025, geschrieben von Alexander Maringer
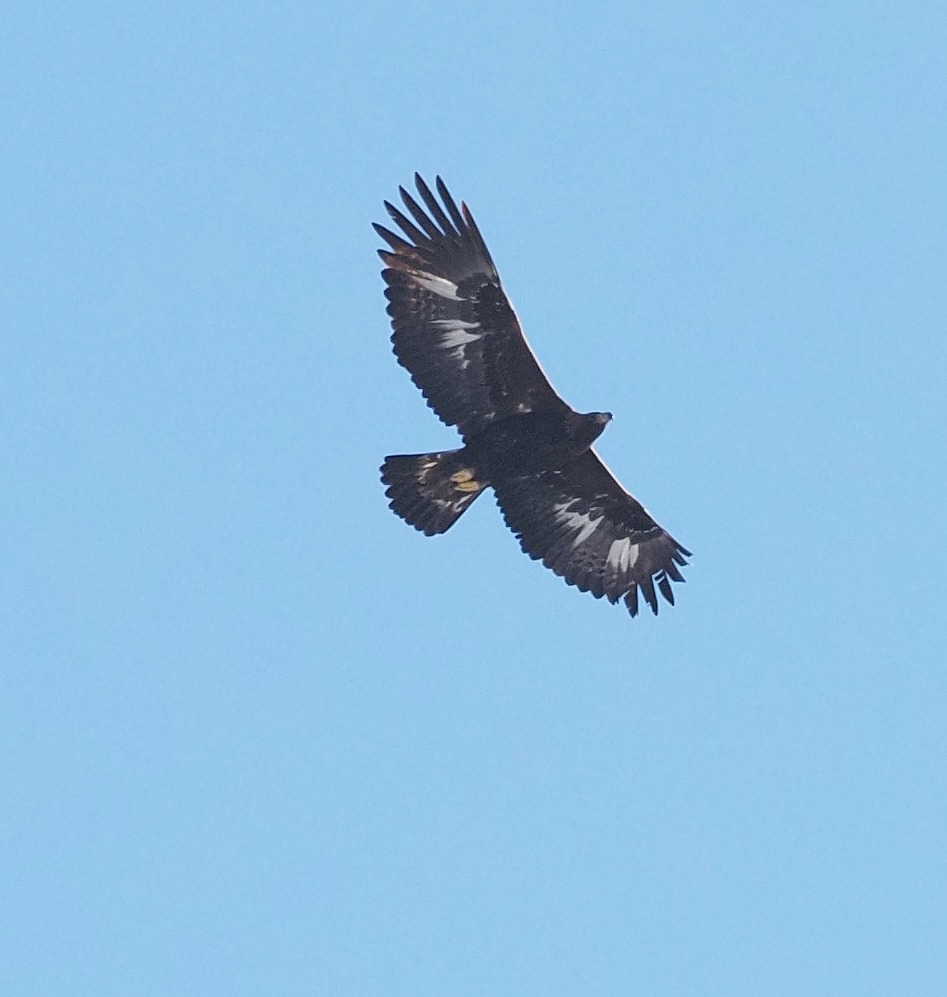

Während die ersten Zugvögel aus dem Süden zurückkehren und die heimischen Singvögel in Brutlaune kommen, ist bei den Wanderfalken und Steinadlern im Nationalpark Gesäuse schon alles ausgemacht! Die beiden Greifvogelarten, die auch im Winter bei uns wohnen, haben die Grenzen ihrer Reviere mit Artgenossen bereits ausgefochten. Nun geht es rasch an das Gelege, das üblicherweise in unzugänglichen Felsen angelegt wird. Dabei suchen Wanderfalken Brutnischen, die meist gar nicht einsehbar sind, und Steinadler bauen, dort wo sich für die großen Vögel genügend Platz bietet, ihre Horste aus Ästen auf. Die genutzten Standorte werden weise gewählt und bleiben oft über Jahrzehnte hinweg gleich. Ein gutes Brutrevier bietet mehrere solcher Horste, die Auswahl spielt also eine Rolle im Leben der Greifvögel.
Zu dieser Jahreszeit sind auch die Mitarbeiter:innen des Nationalpark Gesäuse fleißig unterwegs, um vom Boden aus die Greifvögel zu beobachten. Die Informationen über die Raumnutzung ermöglichen eine vorausschauende Planung von Transportflügen zu Schutzhütten oder Baustellen im Gebiet. Dadurch kann eine Beeinträchtigung auf die Jungvögel abgemindert werden. Denn lärmende Hubschrauber wirken sich nachweislich negativ auf den Bruterfolg von Felsenbrütern aus. Durch das bewährte Miteinander gibt uns die langjährige Brutstatistik aber keinen Anlass zur Sorge.
Infos zum Luftraum und gesetzlichen Regelungen: https://nationalpark-gesaeuse.at/fliegerei/
Heuschrecken zeigen Wert der Lawinenrinnen
Montag, 27.01.2025, geschrieben von Alexander Maringer
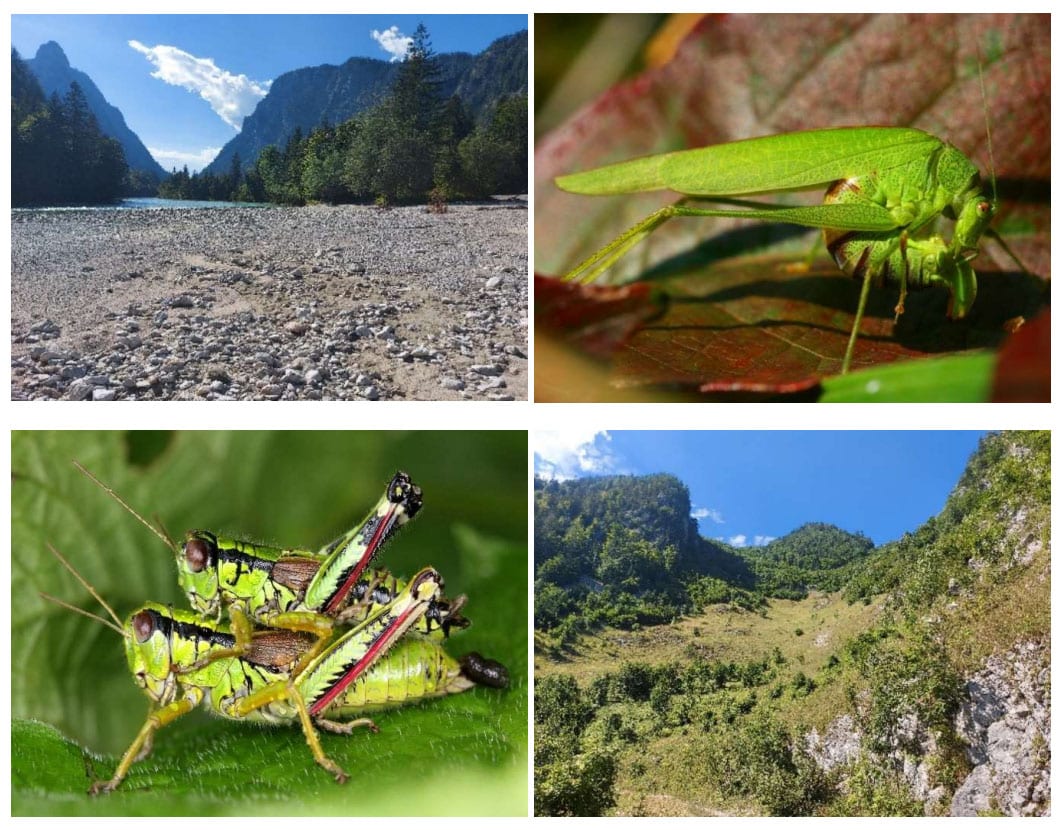

Die sonnigen, wärmebegünstigten Lawinenrinnen an den südlichen Abhängen des Tamischbachturms sind im Nationalpark Gesäuse besonders artenreiche Lebensräume. Das zeigte sich nun erneut in der zu Jahresanfang fertiggestellten Studie. Heuschrecken gelten als Indikatoren für naturschutzfachlich wertvolle Habitate und standen daher im Mittelpunkt dieser Untersuchung.
In den abwechslungsreichen Biotopen der Lawinen wurden 21 Heuschreckenarten, darunter der gefährdete Warzenbeißer (Decticus verrucivorus) und die Gewöhnliche Gebirgsschrecke (Podisma pedestris), nachgewiesen. Beachtliche weitere 10 Arten gelten als nahezu gefährdet, sind also anderenorts bereits sehr selten geworden.
Im Fokus standen auch die Schotterbänke an der Enns und am Johnsbach, die aber aufgrund der Überschwemmung bei Hochwässern nicht so hohe Individuen- und Artenzahlen erreichen. Auf der Mähwiese beim Erlebniszentrum Weidendom traten immerhin zehn Arten auf, was den Grünlandstandort aus heuschreckenkundlicher Sicht auszeichnet, so die Forscher.
Die Experten unterstreichen den naturschutzfachlichen Wert der Lawinenrinnen, in denen die Dynamik langfristig erhalten bleibt. Im Vergleich sind in den letzten 15 Jahren die Artenzahlen leicht gestiegen.
Viel Totholz = viele Pilze
Dienstag, 03.12.2024, geschrieben von Barbara Bock

Im Herbst 2024 fanden die ersten Aufnahmen zum Projekt „Sukzession auf Totholz in der Lettmair Au“ statt. Dabei sollen über die nächsten Jahrzehnte vier unterschiedliche Totholzstämme auf die Artenzusammensetzung von Pilzen, Flechten, Moosen und Gefäßpflanzen im Laufe ihrer Zersetzung untersucht werden.
Die erste Erhebung der Pilze, durchgeführt von Gernot Friebes, erbrachte beachtliche 45 verschiedene Arten, wobei der artenreichste Totholzbaum die Buche mit 25 Pilzen war, gefolgt von der Schwarzpappel mit 16, Fichte mit 10 und Tanne mit 8 Arten. Da die ausgewählten Totholzbäume erst 2 Jahre zuvor von einer heftigen Windböe umgeworfen wurden, ist es nicht verwunderlich, dass die Zahl jener Pilze, die bereits frisch abgestorbenes Totholz besiedeln können, noch entsprechend hoch war. Dennoch konnte die Fundliste durch einzelne Arten ergänzt werden, die länger abgestorbenes Substrat besiedeln, da derartige Stellen bei den meisten Bäumen ebenfalls schon vorhanden waren (vor allem Äste im Kronenbereich).
Neben den zu erwartenden Arten, wie dem Gewöhnlichen Buchenkreisling, ein attraktiver und charakteristischer Bewohner von totem Buchenholz (Bild 1 – oben), sorgten auch einige seltene Pilze für Überraschung. Das Rotstielige Laubblatt-Sklerotium-Fadenkeulchen (Bild 2 – unten) wurde bisher nur zweimal in der Steiermark nachgewiesen. Im Zuge der Erhebung konnte es aber sogar an drei der vier Totholzstämme festgestellt werden!

Neophytencamp 2024
Mittwoch, 07.08.2024, geschrieben von David Gonzalez

Eine der größten Bedrohungen für die Biodiversität der wertvollen Ökosysteme des Gesäuses sind Neophyten, invasive Pflanzenarten. Sie stammen aus anderen Regionen der Welt und können sich in einem neuen Gebiet rasant und unkontrolliert ausbreiten, heimische Arten verdrängen und somit die Dynamik und Diversität dieser Ökosysteme beeinträchtigen. Speziell handelt es sich im Gesäuse um fünf verschiedene Pflanzenarten: das chinesische Springkraut (Impatiens glandulifera), die kanadische Goldrute (Solidago canadensis), die Riesengoldrute (Solidago gigantea), das einjährige Berufskraut (Erigeron annuus) und den japanischen Staudenknöterich (Fallopia japonica).
Der Kampf gegen diese „Aliens“ ist sehr aufwändig, mühsam und zeitintensiv. Wichtig ist, dass sie zum richtigen Zeitpunkt des Jahres bekämpft werden, um ihre weitere Verbreitung und ein erneutes Aussamen zu verhindern.
Um diesen Außerirdischen die Stirn bieten zu können, wurde dieses Jahr Ende Juli die zweite Edition der Invasive Alien Action Days durchgeführt. Dabei handelt es sich um ein einwöchiges Workcamp für circa 15 Teilnehmer aus aller Welt, die uns in diesem Zeitraum tatkräftig beim Kampf gegen die Neophyten im Nationalpark unterstützen. Organisiert wurde das Workcamp in Kooperation mit Service Civil International (SCI), einer Organisation für internationale Freiwilligen-Workcamps.
Dieses Jahr hatten wir viel Glück mit der Wetterlage, trotz angesagten Regens wurden wir nur in der Enns nach einem harten Bekämpfungstag nass. Bearbeitet wurden verschiedenste Flächen über den ganzen Nationalpark verteilt, besonders in sehr schützenswerten Gebieten wie dem Kalktal.
Die Früchte der Mithilfe von den motivierten freiwilligen Helfern wurden schon bald sichtbar. Nennenswert ist die diesjährig erfolgreich abgeschlossene Bekämpfung des japanischen Staudenknöterichs, der mit Abstand der hartnäckigste der fünf Neophyten ist. Somit wurde er beispielsweise ein Jahr mehr daran gehindert in den Johnsbach einzutreten und sich an seinen Ufern auszubreiten.
Belohnt wurden unsere Freiwilligen für ihre Arbeit natürlich auch, unter anderem an ihrem freien Tag mit der atemberaubenden Aussicht bei einer Wanderung auf den Tamischbachturm.
David González
Schneehuhn-Monitoring im Gesäuse
Mittwoch, 26.06.2024, geschrieben von David Gonzalez

Eine der charismatischsten Tierarten des Nationalparks Gesäuse sowie der Alpen insgesamt ist das Schneehuhn. Sowohl gut getarnt in einem Mosaik von Schnee, Fels und alpinem Rasen durch sein ständig wechselndes Federkleid, als auch sehr kältetolerant ist es gut angepasst an das schroffe Habitat oberhalb der Baumgrenze in den Alpen.
Bedingt durch den Klimawandel und menschliche Störungen in ihrem Lebensraum ist ihr Bestand vielerorts jedoch rückläufig. Das Schneehuhn gilt als Klimawandel-Verlierer, da es bei steigenden Temperaturen, im Gegensatz zu Arten niedrigerer Lagen, nicht noch höher in kühlere Lagen ausweichen kann. Um diesen Trend im Nationalpark Gesäuse zu überwachen und den Schneehuhn Bestand bestmöglich zu erhalten, wurde dieses Jahr der erste Schritt hin zu einem langfristigen Monitoring gesetzt. Dass es in unserem Nationalpark Schneehuhn-Populationen gibt, war uns schon lange bekannt, jedoch war es nötig genaue Individuenzahlen an ausgewählten Standorten zu erheben, um so die Populationsgröße zu schätzen und langfristige Trends und Veränderungen erkennen zu können.
Um das zu erreichen wurden dieses Jahr an zwei verschiedenen Standorten innerhalb des Nationalparks insgesamt drei Mal Schneehühner gezählt. Beide Referenzgebiete besitzen je eine Fläche von circa einem Quadratkilometer, wodurch bei jeder Zählung zwischen fünf und sechs Mitarbeiter:innen beteiligt waren, um die Fläche ausreichend abzudecken.
Schneehühner sind dämmerungsaktive Tiere, eine Anpassung um die Aktivitätsphasen ihrer Fressfeinde zu vermeiden. Um die Tiere in ihrer aktivsten Phase beobachten zu können und so die Chance zu nutzen so viele Schneehühner wie möglich zu identifizieren, mussten die Zählungen an den Rhythmus der Tiere angepasst werden. Praktisch hieß das für die Kolleg:innen, vor Sonnenaufgang, um circa 3 Uhr in der Früh aufzustehen und um 4 Uhr mit dem Zählen zu beginnen. Der resultierende Schlafmangel, die Kälte und die Nässe wurden dabei durch die Faszination so seltene Tiere zu beobachten in Kombination mit einem atemberaubenden Sonnenaufgang ausgeglichen.
Vor allem der charakteristische Ruf des Schneehuhns, der stark an das Knarren einer alten Tür erinnert, war die wichtigste Hilfe, um die Hähne im Gelände aufspüren und zählen zu können.
Pro Zählung wurde etwa drei Stunden lang gezählt und direkt danach die aufgenommenen Daten miteinander verglichen. Anhand des Vergleichs und der Auswertung der Daten wurde auf die vorhandene Individuenzahl der Hähne im Untersuchungsgebiet geschätzt. Durch die Anzahl der Hähne kann in der Brutsaison des Weiteren auch auf die Anzahl der Hennen und Territorien geschlossen und so eine Schätzung für die gesamte Populationsgröße der zwei Standorte gewonnen werden.
Die Ergebnisse der diesjährigen Zählung lassen auf 6 bis 7 Hähne in einem und 7 bis 9 Hähne im anderen Gebiet schließen. Weiterführendes Monitoring in den nächsten Jahren wird womöglich einen Aufschluss über die tatsächliche Populationsgröße, ihren Trend im Zusammenhang mit dem Klimawandel, und potenziellen Aktionsbedarf, um sie zu erhalten, geben.
Preise für Forschung im Gesäuse
Freitag, 14.06.2024, geschrieben von Alexander Maringer

Jährlich vergibt Nationalparks Austria Forschungspreise an junge Wissenschaftler:innen. Am 03. Juni 2024 fand die feierliche Urkundenverleihung im Klimaschutzministerium in Wien statt, bei der sich alles um die Forschung in den österreichischen Nationalparks drehte. Die wissenschaftlichen Arbeiten wurden dabei kurz vorgestellt und anschließend die Urkunden überreicht. Die Auszeichnungen zeigen die Vielfalt der Forschung im Nationalpark sehr deutlich:
- Stefan Ulz, TU Graz: Green’s Function Method for the Analysis of Soil Heat Flux in the Mountain Group Gesäuse
- Nora Landl, Universität Graz: Untersuchung der Auswirkungen menschlicher Aktivität auf die geomorphologischen Prozesse des Kühgrabens im Nationalpark Gesäuse unter Verwendung von UAV-Daten
- Moritz Ladurner, Universität Innsbruck: Pflanzengroßrestanalytische Rekonstruktion der spätglazialen und holozänen Floren- und Vegetationsgeschichte im und in der Umgebung des Sulzkarsees
- Angelika Kosjek, Privaten Pädagogische Hochschule Augustinum: Verbesserung des Umweltbewusstseins durch das Partnerschulprojekt des Nationalparks Gesäuse
Mehr zu Abschlussarbeiten und Forschungsanträgen im Nationalpark Gesäuse:
https://nationalpark-gesaeuse.at/nationalpark-mitgestalten/forschungskooperation/
Die Flussuferläufer sind da!
Dienstag, 16.04.2024, geschrieben von Andreas Hollinger

Etwas früher als letztes Jahr trafen am 07. April die ersten Flussuferläufer im Nationalpark ein. Sofort nach der Ankunft stellten sich offenbar auch schon Frühlingsgefühle ein. Was daraus wird, wird sich zeigen. Eine Tafel mit der aktuellen Zahl an Brutpaaren und Jungvögel informiert bei der Beobachtungshütte beim „Leierweg“.
Ptarmigan census - Help us!
Thursday, 08.02.2024, written by Andreas Hollinger

How many ptarmigans currently live in the Gesäuse National Park? We don't know exactly ourselves! For this reason, we will try to count them, or rather, observe individual areas more closely and draw conclusions about the total population.
Have you also spotted ptarmigans in the Gesäuse National Park? Please let us know when and where exactly: To the online form
Master's thesis "Golden Eagle"
Thursday, 21.12.2023, written by Rebekka Kreikenbohm

In her Master's thesis, Rebekka Kreikenbohm analysed the influence of weather and climate on the breeding performance of golden eagles in the Northern Limestone Alps. The analyses included breeding data from 18 years of monitoring in the Gesäuse National Park. Weather influences in the winter before the start of breeding as well as during the egg and nestling phase were analysed. Surprisingly, the eagles began breeding more frequently after cold and rainy weather in winter and had a higher hatching success after similar weather conditions in spring. Although the birds' energy requirements are greater in cold weather, they may have benefited from an improved food supply and reduced human activity during bad weather in the mountains. The effects of climate change, with warmer winters and less snow in spring, could pose challenges for the golden eagles of the Northern Limestone Alps in the future.
The work was carried out as part of the cross-border golden eagle project, which is coordinated by the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behaviour, Radolfzell, in close collaboration with the Swiss Ornithological Institute Sempach and the Konrad Lorenz Research Centre for Behavioural and Cognitive Biology, Grünau im Almtal. The work was supervised by Assistant Professor Dr Petra Sumasgutner (University of Vienna), Dr Matthias Loretto (Technical University of Munich) and Professor Dr Sonia Kleindorfer (University of Vienna).

Master's thesis "Measuring climate systems"
Monday, 30.10.2023, written by Stephan Ulz

Stephan Ulz is a physicist and in his master's thesis he studied essential climate variables that describe the state of the Earth's climate. In his work, he analysed the data from soil temperature loggers in the national park and developed an equation that derives the soil heat flux. This is an important contribution to the understanding of climate change in the national park.
What is the state of the climate system or ecosystems? To answer this question, special state variables have been defined. Important representatives in this regard are the temperature and the heat flow at the earth's or soil's surface. But how do you measure these? You could hold a thermometer to the earth, but then you face the problem that you can no longer tell whether you are measuring the temperature of the soil or that of the air. Besides, you can't tell anything about heat flows with a thermometer. Or can you? So what do you do? You bury the thermometer.
But we still want to know the temperature and the heat flow at the surface of the soil. No problem, mathematics helps us! A bit of modelling, a bit of solving equations and typing the whole thing into the computer. Voilà, we have already found the temperature at the earth's surface, and as an extra we have the heat flow and other important quantities. Soon available in the database.

Caving in the Gesäuse
Tuesday, 10.10.2023, written by Gudrun Bruckner; pictures: E. Herrmann and G. Bruckner

For more than 20 years, members of the Association of Austrian Speleologists have been coming to the Gesäuse Mountains for a week in late summer. Because there is still a great need for research in their field here. Since the karst landscape of the Gesäuse is very steep and rugged, many caves are vertical shafts, which makes access difficult and presents the speleologists with challenges time and again. This year, new cave systems were again explored and mapped. During the survey of the Schneekarei Cave in the Hochtor Group, the researchers penetrated more than 500 metres below the surface. The newly discovered Hollinger Ice Cave, 460 metres long and 60 metres deep, is the largest cave in the Buchstein Massif to date. The researchers were not only active underground, but also documented geological phenomena on the surface. The sediment samples and cave wall remains from the Buchstein could be of great scientific interest. Here sediment profiles were recorded and coal-bearing rock samples collected, from which an age determination is now to be made through pollen remains in the sediment. These results will tell us more about the geomorphological development of the Buchsteinstock. Perhaps there were karst phenomena and cave formation here much earlier than previously assumed.

Rock sample with palaeobiological inclusions

Documentation of the sediment profiles
Mycological hotspot hartelsgraben
Monday, 09.10.2023, written by Gernot Friebes

Due to its abundance of deadwood and high humidity, the Hartelsgraben is undoubtedly one of the most interesting areas of the National Park from a mycological point of view. Although the ditch has already been mapped several times by mycologists, numerous interesting and new species for the area were observed during two inspections this summer. Among them are even five new records for Styria and two first records for Austria, all of them wood-inhabiting fungi: The pale orange stubby foot (Crepidotus ehrendorferi), the head-cell spherical stubby foot (Crepidotus malachioides; see photo), the spindle-cystid bark fungus (Hyphoderma involutum), the round-spored head cystidium Repetobasidium vestitum and the orange-brown spruce layer fungus (Veluticeps ambigua), each new for Styria, as well as the two bark fungi Basidiodendron radians and Peniophorella martinii, which have no German names, as new finds for Austria. Two of the species found are also classified as "endangered" (Cat. 3 - VU) in the Austria-wide Red List, four even as "severely endangered" (Cat. 2 - EN)!
Experiment on bark beetle development
Wednesday, 23.08.2023, written by Alexander Maringer

In the Gesäuse National Park, an experiment on bark beetle development was started at different locations. This involves a box with a fine-meshed net in which a counted number of bark beetles are already present. Only climatic influences have an effect, insects can neither get in nor out. This field experiment complements extensive laboratory work at BOKU in Vienna.
A close look: the Draimännige Grimaldimoos
Friday, 11.08.2023, written by Alexander Maringer

In cooperation with the University of Vienna (Mag. Dr. Harald Zechmeister), the nature conservation student Anna-Lena Hauser is investigating the rock dwarf moss "Mannia triandra", which is native to the Gesäuse National Park. It is an endangered species with special habitat requirements, which is listed in the European Union's Habitats Directive (FFH-RL). From March until the end of the population's survival period, the development of the moss is studied at various sites. The temperature and humidity of the individual sites are also measured. The tiny moss impressively shows how beautiful and exciting even the very small things can be.
BIRD MARkERS TO PROTECT Rough-legged chickens
Tuesday, 18.07.2023, written by Alexander Maringer
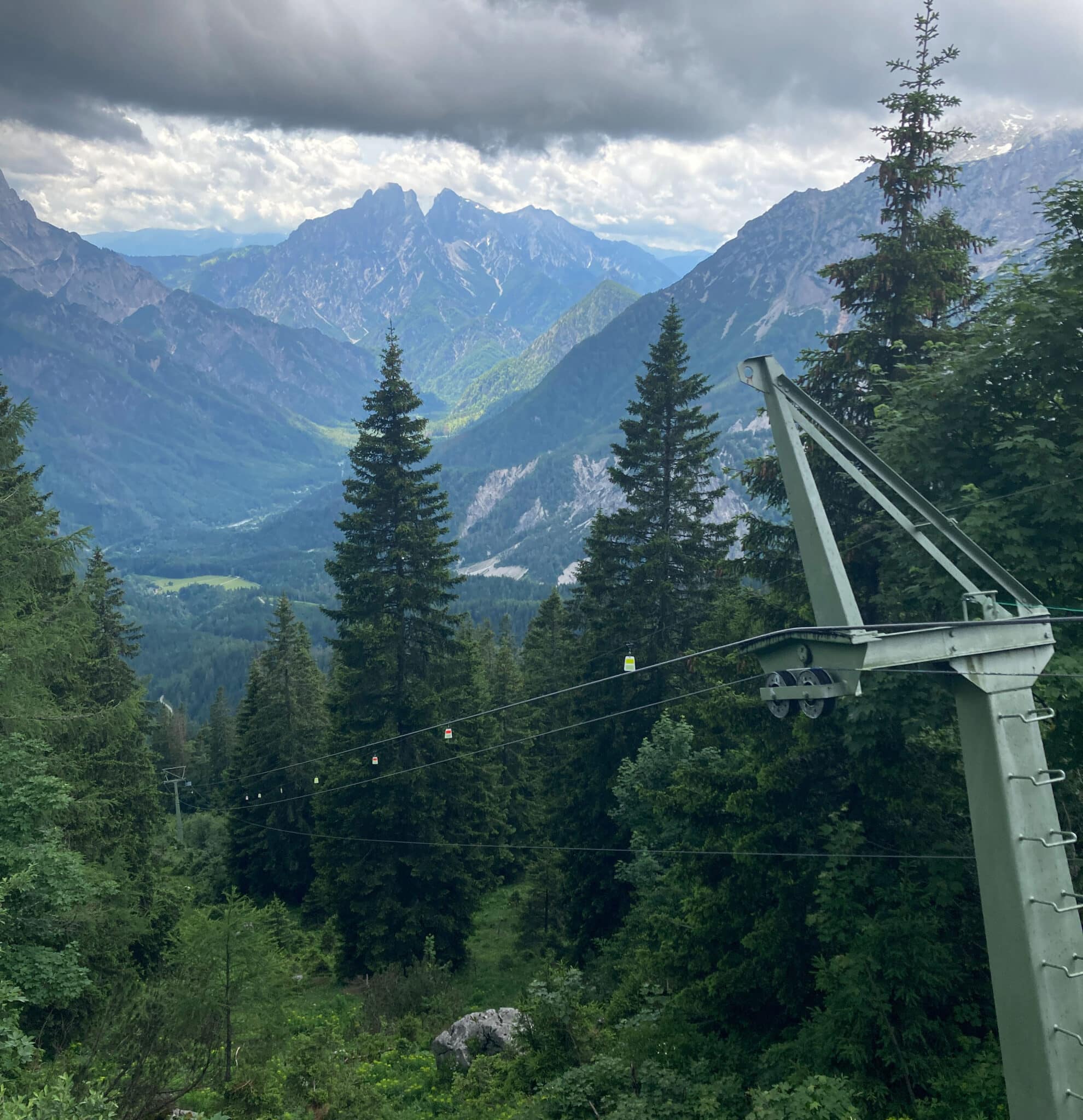

The Gesäuse National Park is home to protected grouse species such as capercaillie and black grouse. Suspension cables or overhead power lines at canopy height pose a danger to the birds. Experts therefore recommend making the obstacles visible to the animals.
One of the capercaillie occurrences in the National Park is in the Gstatterboden basin. If you go higher up, you enter the habitat of the black grouse. Both habitats are intersected by the material cableway to the Ennstaler Hütte. In order to prevent possible collisions, we were able to implement the installation of so-called "bird protection markers" in close coordination with the hut keepers and the Steyr Alpine Club. These are flags made of robust plastic, which are clipped onto an auxiliary rope. They are conspicuously coloured and reflect in order to warn birds flying through of the obstacle.
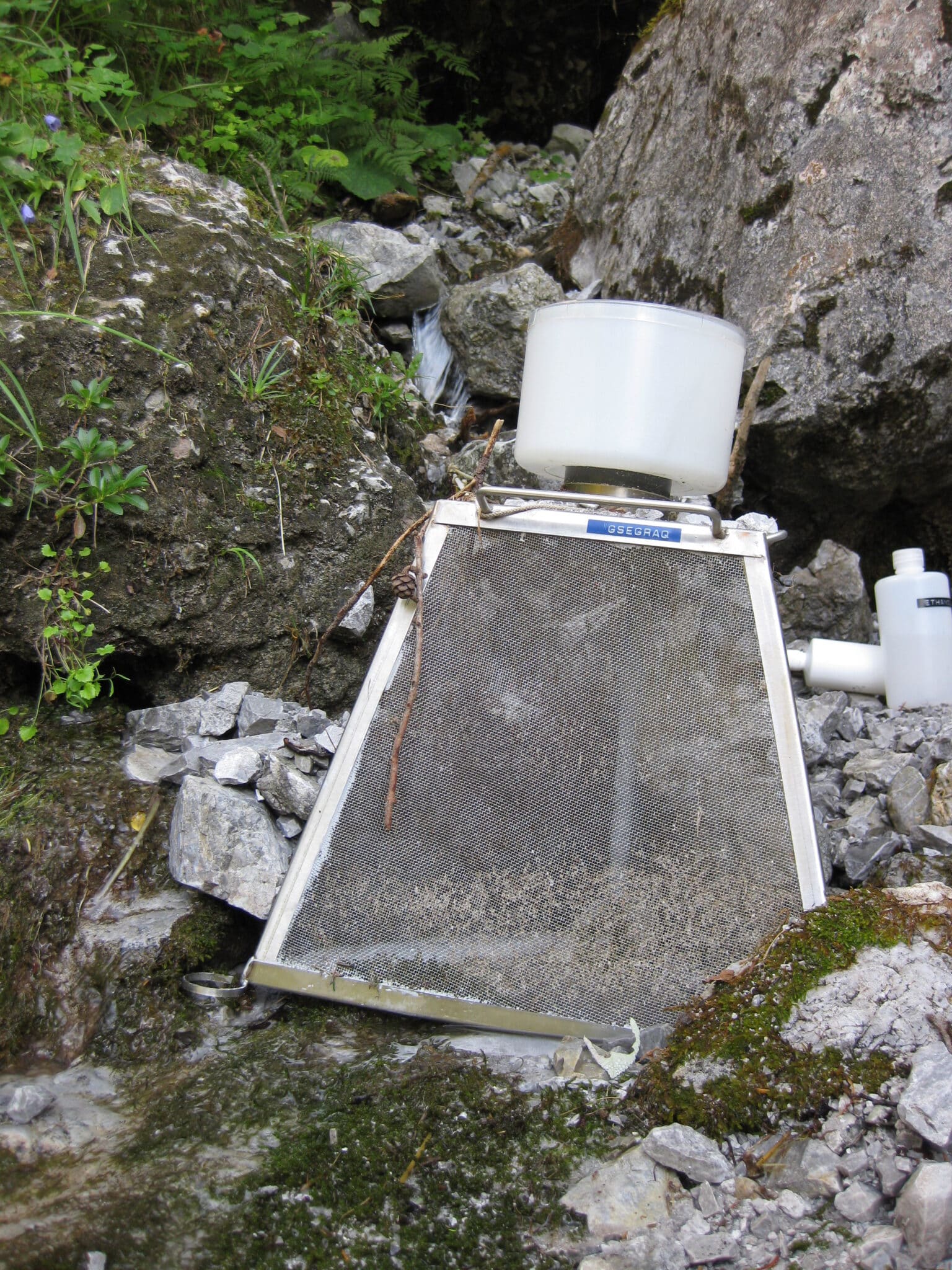
Insect tents for biodiversity data
Wednesday, 31.05.2023, written by Alexander Maringer

A tent-like insect trap was installed above the Kölblalm Hut as part of an EU-wide project. Important biodiversity data is collected here and state-of-the-art DNA methods are also used.
Welcome back Fluffi!
Wednesday, 26.04.2023, written by Alexander Maringer

There is great joy about the long-awaited arrival of the sandpipers in the Gesäuse National Park. These migratory birds fly north from Africa every year and spend the summer in the Gesäuse to breed and raise their young. This year, despite bad weather, the first arrivals were sighted on 12.4. The National Park team celebrated the happy event with Fluffi beer brewed by National Park employee Markus Blank. This was accompanied by Fluffi cake and some funny bird-style disguises.
Two new species for the Gesäuse National Park!
Monday, 19.09.2022, written by Barbara Bock

Two new species for the Gesäuse National Park!
Thanks to a targeted search by the two bryologists Harald Zechmeister and Michaela Kropik, two new moss species of the Habitats Directive Annex II were found this summer. These are the two small, difficult to determine liverwort species Mannia triandra, the rocky grass dimoos, and Scapania carinthiaca, Carinthian Spade Moss. Mannia triandra was found at seven locations within the national park. Scapania carinthiaca at least three. Neither species seems to be endangered in the National Park. The high site dynamics are very favourable to them here: As species with low competition, they are dependent on newly created small sites where competition is still low. Local extinctions can be compensated for by recolonisation if there is a sufficient supply of new replacement sites. The Gesäuse National Park has a high responsibility for the survival of both species in Austria and Europe due to its natural conditions and the vital populations of both species.
Gesäuse research top internationally
Thursday, 15.09.2022, written by Alexander Maringer, photo by Aslan Kudrnofsky

Under the title "Protected areas confront the biodiversity crisis", the National Parks Austria Research Symposium took place from 7 to 9 September on the campus of the University of Vienna. Over 100 researchers presented their work from international protected areas. The focus was on the role of protected areas in global change, wilderness development and modern biodiversity research.
Christian Komposch (Ökoteam), Dorian Shire-Peterlechner (BOKU), Tobias Köstl (E.C.O.), Robert Schabetsberger (Uni Salzburg) and Christina Remschak, Magdalena Kaltenbrunner and Alexander Maringer contributed to the Gesäuse research. The networking of the Gesäuse National Park with other research groups, such as Austrian Barcode of Life (ABOL) and Global Observation Research Initiative in Alpine Environments (GLORIA), became visible in many other presentations.
The conference was attended by 350 participants. The programme consisted of 25 sessions with 106 individual presentations, numerous poster contributions and four excursions. Highly topical issues such as the state of the sodalacks in the Neusiedler See - Seewinkel National Park and its consequences for water birds were discussed as well as the pioneering work of fungi in the natural balance or the potential of new technologies in research.
National Parks Austria Research Award
Geoelectrical monitoring in a limestone-alpine gravel body,
written by Raphael Glück

Nationalparks Austria Research Award: Geoelectrical monitoring in a calcareous alpine gravel body
This case study deals, using geoelectric monitoring, with the measurement of electrical conductivity in a calcareous alpine gravel body. The change in electrical conductivity was monitored from November 2019 to October 2020 (nine field campaigns) in a gravel trench in the Gesäuse National Park (Johnsbachtal, Styria) during Raphael Glück's master thesis.
On the trail in the gravel
The Langgriesgraben in the Reichenstein Group is part of a channel with high morphodynamic activity, which drains into the Johnsbach running across the ditch. The Langgriesgraben, filled with main and Wetterstein dolomite, slope debris breccias and Raibler strata, has a powerful groundwater body, the size and location of which is influenced by precipitation events. The change in the groundwater body as well as the rise and fall of the groundwater level can be derived from the specific electrical resistance. The geoelectrical resistivity measurement in this work is carried out with the Wenner configuration, in the data evaluation with Res2Dinv the least squares and time-lapse inversion methods as well as bedrock detection were used.
The electrical conductivity
By means of 17 profiles, with four or two metre electrode spacing, it could be shown that the electrical conductivity in the Langgriesgraben changes strongly in the course of the year due to climatic conditions. Repeat measurements have shown that the electrical conductivity decreases more strongly in summer at the surface of the Langgriesgraben than in the underlying layers. During frequent precipitation events, the electrical conductivity increases and leads to an increasing water saturation of the unconsolidated sediments in the gravel body and to the regulation of the position and thickness of the groundwater body. The comparison of meteorological data of the WegenerNet in the Johnsbach valley could also show that the electrical conductivity increases significantly in autumn, both on the surface and in the subsurface.
Info on the National Parks Austria Research Award
Text and photo: Raphael Glück
Students discover biodiversity
Monday, 22.08.2022, written by Barbara Bock and Gernot Kunz

Students discover biodiversity
As part of the new course "Excursions to the Fauna of Austria", students at the University of Graz, under the direction of Dr. Gernot Kunz, learn about the native fauna in the most diverse habitats of Styria. At the end of July, the Gesäuse National Park with its unbelievably rich endemic fauna was also the destination of this course.
Three UV light towers were set up in the area of the Ennsbodenweg to attract moths & co. In addition, the students searched the surrounding area for any animals on the ground, in the bushes and on the trees.
Thus, in only four hours from 20:00-24:00 and despite less than optimal weather conditions, a total of 700 animals could be observed, belonging to about 200 different species. Among them are the EU-protected Spanish Flag (Euplagia quadripunctaria), as well as the Schönbär (Callimorpha dominula) and two red-coloured ribbons (Catocala nupta and Catocala erecta). In order to make the collected data sets scientifically available, all animals were documented photographically and georeferenced and uploaded to the iNaturalist reporting platform.
All these finds can be found on the project page "Biodiversity in the Gesäuse National Park" can be browsed publicly.
Successful premiere
Wednesday, 25.05.2022, written by Magdalena Kaltenbrunner

The City-Nature-Challenge 2022 is over. In the successful worldwide campaign, almost 1.7 million observations of more than 50,000 species, including around 2200 endangered or threatened species, were documented in four days.
The Gesäuse did very well with 1330 observations of 457 species, placing it in the good midfield worldwide and in 7th place in Austria!
By the way, wood cowslip, snow lily and liverwort are the species we noted most often. We found endangered species such as the blue ground beetle the most exciting.
Many thanks to all who participated diligently. First and foremost, thanks to the Junior Rangers, who spent a day criss-crossing the area with their mobile phones! Next year we will certainly take part in this international challenge again - the Gesaeuse region is a biodiversity hotspot and there is a lot to discover.
Welcome back! The riverside runners are back!
Thursday, 05.05.2022, written by Magdalena Kaltenbrunner

Every year in spring, the sandpipers make the long journey north to spend the summer in the Gesäuse and raise their young. After the first arrivals of the year were spotted on 13.4, there was a "Fluffy Welcome Drink" in the Weidendomhütte to celebrate. With Markus Blank's home-brewed Fluffy beer, the National Park staff toasted to a hopefully successful breeding and monitoring season.
Detection and mapping of grayling
Wednesday, 30.03.2022, written by Sarah Sturm

Sarah Sturm conducted research for her diploma thesis in the Gesäuse National Park, where she wanted to find out whether grayling (Thymallus thymallus) ascend into the Johnsbach or not.
Within the framework of a diploma thesis, sections of the Enns and the Johnsbach in the area of the "Gesäuse National Park" were sampled between the end of April and the end of May. The primary aim was to test whether grayling (Thymallus thymallus) rise into the Johnsbach or not. To determine this, the eDNA qPCR protocol was used or tested.
Sampling was carried out at a total of five sites, three of which were in the Enns and two in the Johnsbach. These easily accessible sites were chosen so that the sandpiper ((Actitis hypoleucos)) was not disturbed while breeding.
The sample sites in the Johnsbach were right next to the car park of the "Bachbrücke" inn and the "Hellichter Stein" visitor car park. The coordinates were determined using a GPS device (Garmin GPS MAP® 64) and checked and illustrated with the help of the digital Styrian atlas.
The first sampling point of the Enns was on the right bank of the river before the "Johnsbach - Steg" and after the mouth of the Enns / Johnsbach. The second sampling point was at the entrance to the white-water rafting course and the third at the campsite "Gstatterboden" shortly after the bridge.
At each sample site, a total of 1 litre of water was forced through the filter to collect the eDNA. The samples were then extracted in the laboratory and tested by qPCR to see if they contained grayling DNA.
The protocol worked in both the Enns and the Johnsbach, as at least one replicate amplified at each site. It was thus established that the protocol also works in larger rivers such as the Enns, where the grayling population density is low in relation to the size of the river. Even in the Johnsbach, where no grayling were expected, a few replicates amplified, so it can be assumed that grayling ascend at least as far as the sample site "Hellichter Stein".
(Dis)order in nature
Wednesday, 26.01.2022, written by Alexander Maringer

Do we expose ourselves to uncontrollable danger if we stop dominating the landscape around us? Or do we ensure our own survival if we change our perspective and give nature more space?
With the help of many high-calibre contributions, this new book sheds light on the National Park core theme of "wilderness". The development of the Gesäuse National Park over the past 20 years, experiences from other areas such as the Swiss National Park and the expertise of Austrian scientists show what could still await the Gesäuse on its way to wilderness.
(Un-)Ordnung in der Natur - Volume 16 of the "Schriften des Nationalparks Gesäuse" - is now available in our National Park Shop at the price of € 24.90 plus shipping costs:
The home of the peregrine falcons
Thursday, 16.12.2021, written by Magdalena Kaltenbrunner

The striking raspberry stone is an excellent nursery for our peregrine falcons. We know this for a fact, because this year a pair of peregrine falcons successfully nested here and three young birds fledged at the end of May. It takes a lot of experience and patience to spot the agile and well-camouflaged flyers from a great distance against the background of the same colour. If you got too close to them, they would react very sensitively and perhaps give up their nursery in the Gesäuse forever. Therefore, the Raspberry Rock is taboo as a climbing rock.
A good year for the shore tamarisk
Tuesday, 05.10.2021, written by Magdalena Kaltenbrunner

A discovery we made in autumn gives us hope. Four years after the reintroduction of the first riparian tamarisk in the Gesäuse, seedlings were found for the first time this year!
Seeds have germinated in the immediate vicinity of an already stately specimen. Riparian tamarisk is a pioneer plant. Their strategy is to invest energy in a very large quantity of seeds. However, the longevity of the seeds suffers as a result. If the conditions in the germination bed, i.e. subsoil, moisture and temperature for seed ripening are not optimal, the seeds cannot wait for better times, but die. However, this summer and the location probably fulfilled all conditions, so that at least 15 seedlings could grow into approx. 10 cm tall plants in one place.
The Digital Twin
Tuesday, 28.09.2021, written by Magdalena Kaltenbrunner

Sounds like a hacker attack, data theft and internet fraud. But fortunately it is quite different. Researchers are constantly looking for efficient, fast and better methods of data collection. One promising approach, which can be applied in architecture, mechanical engineering but also agriculture, forestry and nature reserves, is terrestrial laser scanning. A device emits several 100,000 laser beams per second and uses them to scan its surroundings. The direction and distance to each surface is stored. The resulting point cloud can be viewed and evaluated three-dimensionally on a PC. It is an exact copy of the forest stand on the PC, hence "digital twin".
The method is suitable for measuring trees precisely, assessing crown and trunk, calculating volumes and much more. However, even years later, the digital twin can still be studied down to the smallest detail, special features can be elicited from it and comparisons can be made. Perhaps in the future it will even be possible to have all data automatically evaluated by the computer and thus to get to the bottom of the secrets of forest growth even better.
Neophyte control in the Gesäuse National Park
Monday, 23.08.2021, Guest article by Anja Brunner, Lisa Neubauer and Judith Quirgst (teacher training programme for biology at the University of Vienna), researched and created in the course of the excursion week in the Gesäuse

On the first day of our small research task, we dealt with the control of the hawkweed, Impatiens glandulifera. In Gstatterboden, near the Forstgarten campsite, we carried out six vegetation surveys measuring 3×3 metres according to Braun-Blanquet - three areas with and three areas without neophytes. Afterwards, we pulled out the knapweed and hung it on trees to dry. This method is sufficient for annual touch-me-not. However, since the seeds can remain germinable in the soil for up to 5 years, control must still be repeated several years in order to successfully suppress the invasive neophyte.
On the second day, we dealt with the neophyte control of Japanese knotweed, Fallopia japonica. Immediately next to the Enns on a sandbank we laid a 25 m long transect in an area of tall herbaceous vegetation. Four vegetation patches were recorded along this line. As on the first day, we identified all species present. The Japanese knotweed is treated annually by the National Park team. Since the smallest pieces of rhizome can immediately grow out again, the plant parts have to be thermally composted.
Overall, no significant correlation between the occurrence of neophytes and species diversity could be proven. However, this could be due to the fact that the National Park has been combating the neophytes at these sites for several years, thus also steadily reducing the populations. These less dense neophyte stands may have no or only minimal influence on biodiversity. Thus, our results would be a good sign of the success of the National Park team in combating neophytes!
However, we were able to establish that there are correlations between the occurrence of certain species. Together with Impatiens glandulifera the great touch-me-not (Impatiens noli-tangere) and also the stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) and the common butterbur (Petasites hybridus). With regard to the occurrence of the lesser touch-me-not (Impatiens parviflora) and Impatiens glandulifera a negative correlation was found.
It was noticeable that the common butterbur (Petasites hybridus) and Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica) do not occur together on a recording surface. It cannot be determined which of the two species was here first, so to speak, or displaces the other. But they are obviously competitors that exclude each other in their simultaneous occurrence.

A month under the spell of golden eagles, sandpipers and co.
Tuesday, 03.08.2021, written by Julia Balasch

"In May (and for corona-related reasons also for a week in July) I was allowed to accompany the work of the National Park's Nature Conservation & Research Department as a volunteer. We started on the very first day with a short snowshoe hike to Lake Sulzkar to count amphibians, and the rest of the time was just as exciting - with the observation and recording of this year's golden eagle and common sandpiper populations, wild camera evaluations and neophyte care missions. Along the way, we were also able to attend project meetings and construction surveys and thus gain even better insights into the day-to-day work of the department. Besides breathtaking experiences in nature and the opportunity to gain a lot of new knowledge and experience, I especially enjoyed the pleasant working atmosphere.
Thank you for a wonderful time!"
Thank you Julia for your help and the time you have given free of charge for nature in the Gesäuse National Park!
In the Gesäuse there are many opportunities to help shape the National Park. Be it in the course of final theses, in the youth advisory board or internships and voluntary work:
Common sandpiper visibly at ease
Monday, 2021-06-21, written by Alexander Maringer

We have been working intensively for years to ensure that sandpipers find quiet breeding areas in the Gesäuse. It seems that we are succeeding more and more through the proven guidance of visitors. For this we say a big thank you!
At the time of the founding of the Gesäuse National Park, around five breeding pairs were confirmed each year; ten years ago, the low of two pairs caused concern. Now we are happy again about 7-8 breeding pairs along the Enns between the Gesäuse entrance and Gstatterboden. That doesn't sound like much, but it accounts for more than a quarter of the breeding population in Styria and is the largest known breeding occurrence in the state!
You can find more about our natural phenomena and the animals in the Gesäuse National Park here. How to behave so that you do not disturb the sandpiper, we summarized in the Fair Play Folder .
We protect Austria's natural heritage
Tuesday, 2021-05-25, written by Alexander Maringer

Since their foundation, the six Austrian national parks have been recording the diversity of their fauna and flora. In a joint project, the Federal Environment Agency and the Department of Botany and Biodiversity Research at the University of Vienna now analyzed these data.
Austria's national parks occupy just under 3% of the country's land area, but complement each other in protecting biodiversity. While the hotspots of vertebrates are located in the national parks Seewinkel and Donau-Auen, the inner alpine national parks are characterized by species diversity in endemics, plants and habitats.
However, the study authors also note that climate change, invasive species, and air pollutants do not stop at any national park boundary. The task of national parks to maintain natural ecosystem processes, on the basis of which species and habitats can persist, is complicated by many human interventions outside national parks.
The most important facts about the study: www.nationalparksaustria.at/unsernaturerbe
Full Report: http://www.parcs.at/npa/mmd_fullentry.php?docu_id=42247
19.05.2021
Networking meeting Eisenwurzen
Networking meeting Eisenwurzen
Research in the region - research for the region
For more info on the workshop, click the link below.

Alpine hotspot of biodiversity
Thursday, 2021-04-22, written by Alexander Maringer

We do not always succeed in making our research results accessible to such a broad audience. But when a major Austrian daily newspaper picks up on a scientific paper, we are particularly pleased.
Read them:
Windkantenrasen - say what?
Tuesday, 2021-03-23, written by Alexander Maringer

Wind energy plays a central role in the mountains. No, we are not talking about wind turbines now. Especially at ridges and summits often a strong breeze blows. Plants growing in this area must be well adapted to cold anyway, because especially in winter life near the summit is extremely hard. When the snow is blown away, it is really icy. The low temperatures and the ice crystals whirled up by the wind act like a sandblaster. If you want to survive up there, you need special protective mechanisms. The plants therefore stay close to the ground, form robust leaves and often grow in compact pads.
Plant communities that grow in such extremely windy places and whose plants have these adapted characteristics are called wind edge grasslands. In 2020, exactly these special species communities were documented in a study at the Tamischbach Tower.
To download the entire research paper, visit the Data Center:
New bat species detected
Monday, 2021-02-15, written by Alexander Maringer
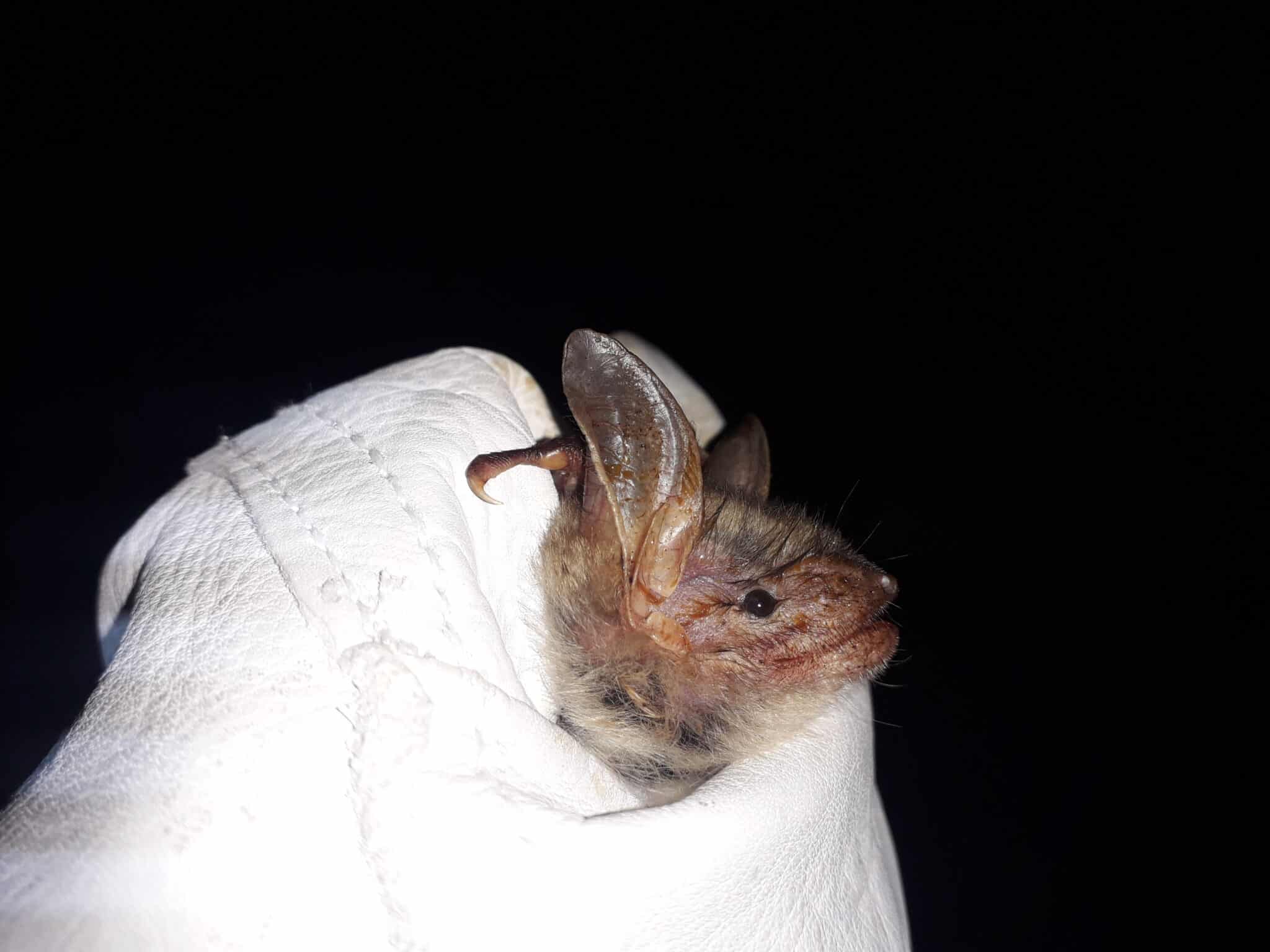
In the Gesäuse National Park, the first record of the "lesser mouse-eared bat" was made. The species inhabits only a very small area in Austria and is threatened with extinction. This bat species lives in large colonies together with its sister species, the mouse ear, in summer and is therefore very difficult to detect. The new evidence from the National Park is therefore particularly valuable.
For the researchers, the demanding terrain and the large number of caves during the two-year study naturally pose a challenge. In the Gesäuse National Park, a total of 18 species have been detected, compared to 26 bat species in Styria as a whole. This is an impressive number for a mountain habitat. The unspoiled mountain landscape but also the traditional alpine pastures are a refuge for many species and the quiet winter quarters in the rocky niches and caves of the Gesäuse are particularly appreciated by the bats.
To download the entire research paper, visit the Data Center:
Winter authorities for nature conservation
Monday, 2020-12-21, written by Alexander Maringer

We are there for you
"We are there for you!" say the national park authorities to the grouse. The Gesäuse National Park is also supervised during the winter months. The sworn organs take care of the ski routes and their signposting, monitor compliance with legal regulations and are contact persons* for everyone who visits us.
When trees grow into the sky
Tuesday, 2020-09-01, written by Alexander Maringer

The Himmelstoß fir is well on its way to growing into the sky. A measurement showed that it is an astonishing 47 meters tall and has a massive circumference of 3.95 meters at chest height!
However, this is not quite true, because trees cannot grow into the sky. This is due to physics. Leaves evaporate water. Evaporation ensures that water can be drawn from the roots into the crown via complicated conduits. However, the higher the tree gets, the more difficult it is to transport the water that far up, and at some point a limit is reached where gas bubbles would form and the system would no longer work. That's why trees - not even the Himmelstoß fir - don't grow to the sky.
P.S.: This fir is named after the legendary forestry director Franz Himmelstoß, head of the Steiermärkische Landesforste forestry operation from 1953 to 1967, who campaigned massively and emphatically for the preservation of the strong solitary trees.
Dare to look into history with wood
Tuesday, 2020-08-20, written by Magdalena Kaltenbrunner

Many secrets lie dormant in Sulzkar Lake. For example, two spruce logs have been lying in the lake for almost 1400 years. As part of the Sulzkarsee project, one piece of each was recovered and has now been dated.
Trees produce wood during their lifetime. In our latitudes, this wood growth is interrupted during the winter half-year. This results in clearly defined annual rings and, depending on the weather sequence over several years, a unique pattern that is recognizable in all trees of a wood species and region. The pattern can be used for dating.
The two logs from Sulzkarsee in the Gesäuse National Park fell into the lake in the years after 617 and 590 AD, respectively, and were at least 150 and 377 years old. The older one was therefore already standing on the lakeshore around the year 200 AD!
Tear-out-dig-out-dispose
Monday, 2020-08-03, written by Barbara Bock
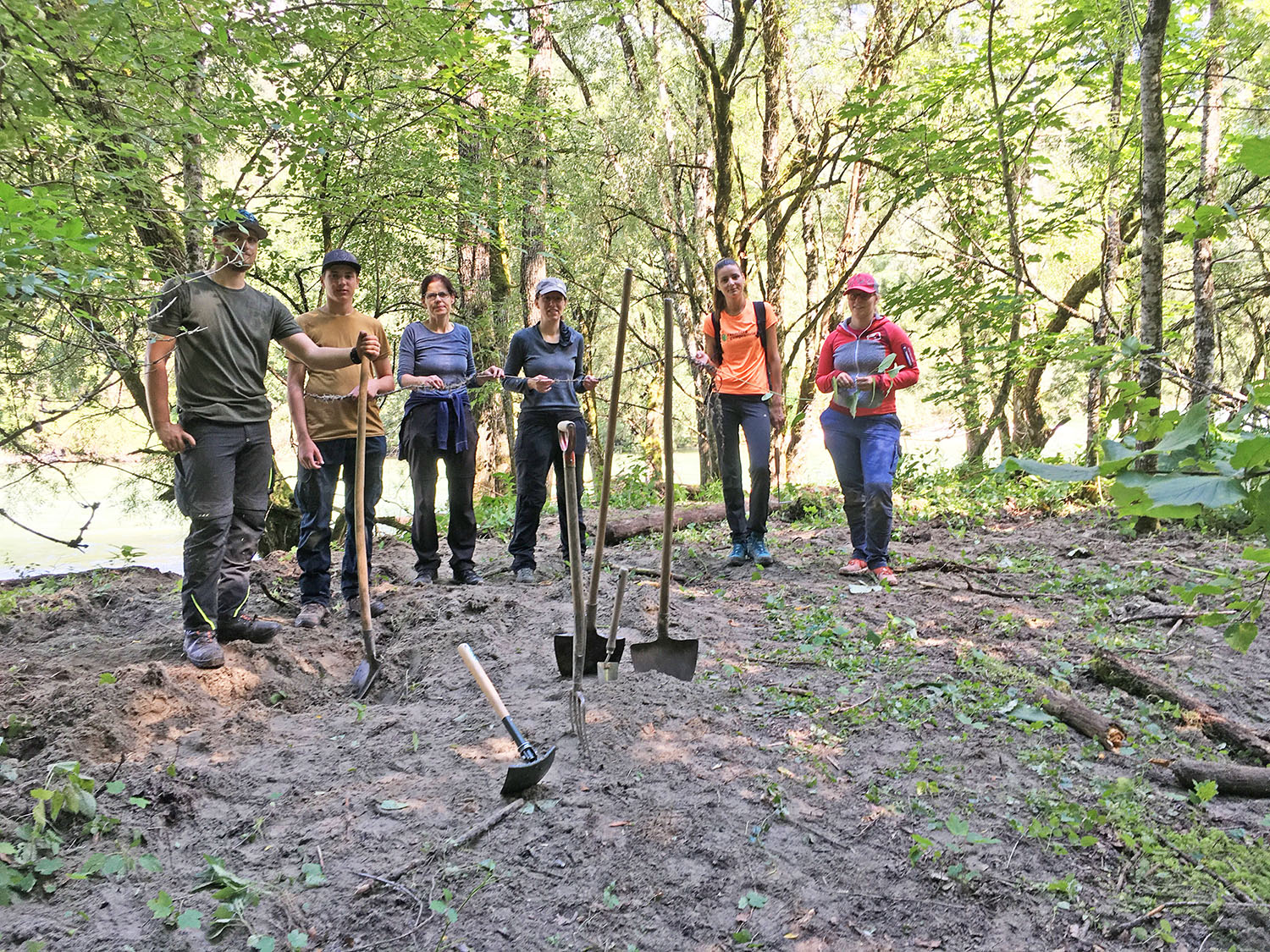

At the end of July, a team of 7 people went out with spades and shovels to once again get to grips with an occurrence of Japanese knotweed in the national park.
Japanese knotweed is considered a highly invasive neophyte that affects the diversity of our plant and therefore animal life through its rapid growth and large-scale spread.
To bring knotweed to its knees, it must be dug up as deep as possible. This is easier said than done - meter-long rhizomes and deep-reaching roots make the task difficult. And last but not least, the battlefield must be thoroughly cleaned up, because a small, forgotten piece of stem can develop into a complete plant again within a short time.
The knotweed stand on the Enns River was treated for the third time this year and the control measures are showing initial success. In the meantime, its growth has been reduced by two thirds. A total of nine garbage bags, each containing 80 liters of plant material, were removed and taken to the waste management association in Liezen for proper disposal.
In fall, there is still a follow-up inspection to remove any new shoots.
The Neophyte Action Day took place, as in previous years, in cooperation with the HBLFA Raumberg-Gumpenstein. Many thanks for your great support!
Natural dynamics during thunderstorms
Tuesday, 2020-07-07, written by Alexander Maringer
During a violent thunderstorm, not one stone is left on the other...
The normally dry stream bed of the Haindlkar turns into a torrent of water, mud and debris within minutes during heavy rain. The way to the Haindlkar hut is then life-threatening and impassable.
The Weissenbachl east of Gstatterboden is a small, clear stream. This changes abruptly during a thunderstorm. Water, mud and debris make their way down to the Enns. The video is from July 1, 2020, with thanks to Christoph Strobl from AOS rafting. www.rafting.at
New butterfly species named after Gesäuse researcher!
Wednesday, 2020-02-19, written by Barbara Bock

In science, new species are sometimes named after deserving personalities. Recently, a new butterfly species from Iran was given the name of the Styrian butterfly researcher Heinz Habeler, who died in 2017.
"In honor of Heinz Habeler, one of my mentors, we named a Noctuid species from Iran after him", writes Benjamin Wiesmair of the Tiroler Landesmuseum about the new type "Orthosia habeleri".
Habeler has spent decades researching the butterfly diversity in Styria and was very attached to the Gesäuse National Park. His book on a total of 1,234 butterfly species in the protected area was published at the end of 2017.







